In Java Swing, the MatteBorder class is used to create a border with a solid color that has a matte-like finish. It is a subclass of the javax.swing.border.Border class and is included in the javax.swing.border package.
To use the MatteBorder class, we first need to create an instance of it by specifying the border width, insets, and color. The border width is the thickness of the border in pixels, the insets define the distance between the border and the component’s edge, and the color specifies the color of the border.
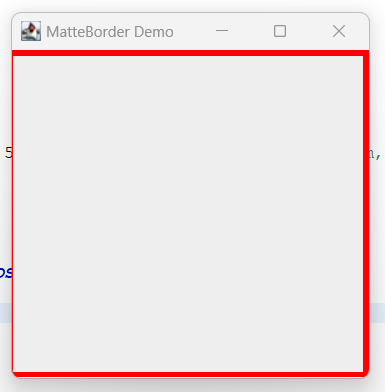
Following is an example of how to create a MatteBorder with a width of 5 pixels to all the corner except left corner, and a red color:
import java.awt.Color;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.border.MatteBorder;
public class MatteBorderDemo extends JFrame {
public MatteBorderDemo() {
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
MatteBorder border = new MatteBorder(5, 1, 5, 5, Color.RED);// top, left, bottom, right and color
panel.setBorder(border);
add(panel);
setTitle("MatteBorder Demo");
setSize(300, 300);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MatteBorderDemo();
}
}In this example, we create a JPanel and set its border to a MatteBorder with the specified properties. We then add the panel to the JFrame and set the frame properties. When we run the program, we see a red border around the panel with a matte-like finish.
Output:
Reference: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/uiswing/components/border.html