Passing data from a JSP (JavaServer Pages) to a Servlet is a common task in Java web development. This guide will walk you through the process in a way that’s easy to understand, especially if you’re a college student just starting with Java web applications.
Prerequisites
- Install and Set Up Java Development Environment
- Set Up Eclipse with Tomcat Server for Java Web Development
Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s break down the process into simple steps:
Step 1: Create a JSP Form
First, you need a JSP page with a form where users can input data. This form will send data to the servlet.
Example JSP (index.jsp):
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Data Input Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Enter Your Details</h1>
<form action="DataServlet" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="name"><br>
Age: <input type="text" name="age"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>In this form:
- The
actionattribute specifies the servlet URL pattern (DataServlet). - The
methodattribute is set topostfor secure data transmission. - Input fields for
nameandageare provided for user input.
Step 2: Set Up a Servlet
Next, create a servlet that will handle the data submitted from the JSP form.
Example Servlet (DataServlet.java):
package com.codersathi;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* Servlet implementation class DataServlet
*/
@WebServlet("/DataServlet")
public class DataServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// Retrieve data from the request
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
// Set response content type
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
// Generate response
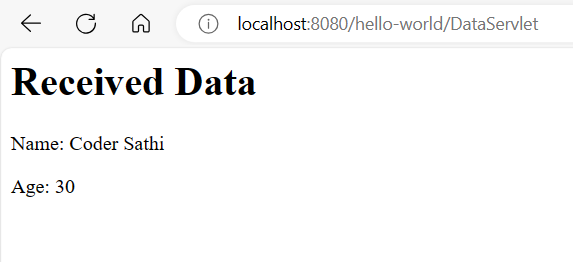
out.println("<html><body>");
out.println("<h1>Received Data</h1>");
out.println("<p>Name: " + name + "</p>");
out.println("<p>Age: " + age + "</p>");
out.println("</body></html>");
}
}
In this servlet:
- The
doPostmethod handles POST requests from the JSP form. request.getParameter("name")retrieves the value of thenameinput field.request.getParameter("age")retrieves the value of theageinput field.- The servlet generates an HTML response displaying the received data.
Step 3: Run and Test Your Application
3.1. Run your application
Use an IDE like Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA to deploy your web application to a servlet container like Apache Tomcat.
3.2. Access the JSP Form
Open your web browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080/YourProjectName/index.jsp.
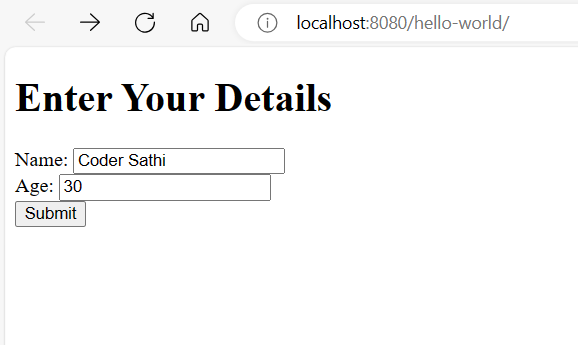
3.3. Submit Data
Enter data in the form fields and click Submit button to send data to Servlet.
3.4. View the Response
The servlet processes the submitted data and displays it in the browser.