AWT and swing are the Java API and both can be used to create a Graphical User Interface (GUI) based application in Java. The Java Foundation Classes (JFC) are a set of GUI components that simplify the development of Desktop applications.
The AWT API-related resources like Class and Interfaces are available in java.awt package and Swing API-related resources are available inside javax.swing package.
The package javax means the extension of the Java Standard Extension.
Main differences between AWT and Swing
| AWT | Swing |
| AWT API is available from Java version 1.0. | Swing API is added in a later version of Java Standard Edition 1.2. |
| AWT components are platform-dependent. | Swing components are platform-independent. |
| It provides fewer components than Swing. | It provides more powerful components like Table, List, Scrollpane, color chooser, tabbed pane, and so on. |
| AWT components are heavyweight. | Swing components are lightweight. |
| AWT does not support a pluggable look and feel in its components. | It supports a pluggable look and feels. |
| AWT does not support the popular design pattern called MVC (Model View Controller). | Swing supports and follows the MVC pattern. |
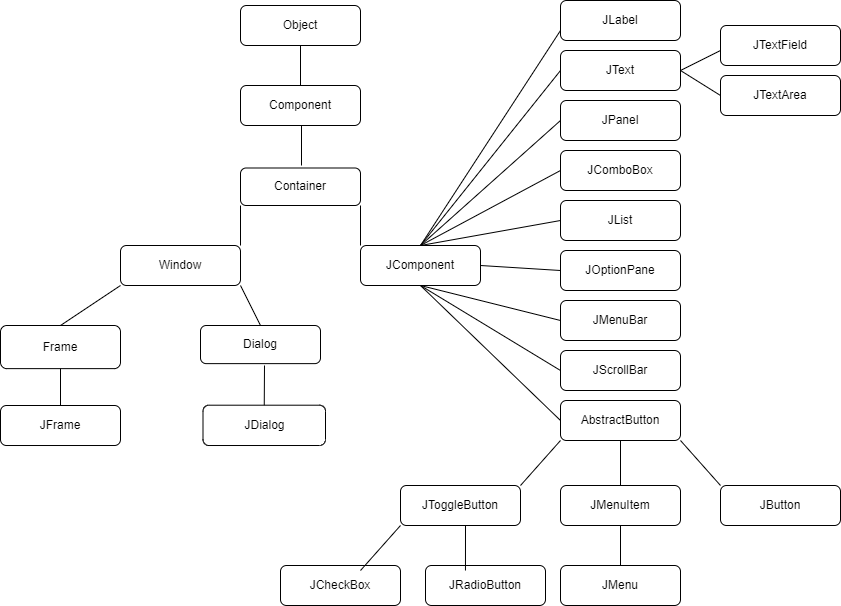
Hierarchy of Java Swing classes
Common methods in Component class
| Method | Description |
public void add(Component c) | Adds a component to another component. |
public void setSize(int width, int height) | Sets the size of the component. |
public void setLayout(LayoutManager lm) | Sets the layout manager for the component. |
public void setVisible(boolean b) | Sets the visibility of the component. The default value is false. |
