Inheritance in Java is a cornerstone of object-oriented programming (OOP) that allows classes to inherit properties and behaviors from other classes. By creating hierarchical relationships, inheritance promotes code reuse, reduces redundancy, and simplifies maintenance. In this guide, you’ll learn how to implement inheritance, use method overriding, avoid common mistakes, and follow best practices for clean, scalable code.
Table of Contents
What is inheritance?
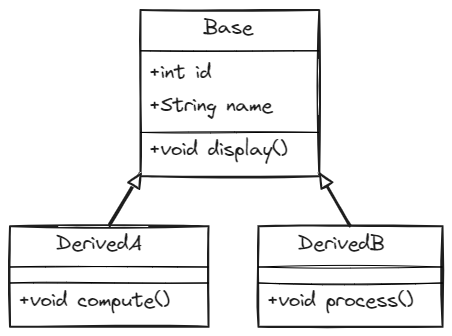
Inheritance in Java enables a subclass (child class) to inherit fields and methods from a superclass (parent class). It follows an “is-a” relationship (e.g., a Car is a Vehicle).
Key Terms:
- Superclass: Parent class whose features are inherited.
- Subclass: Child class that inherits from the superclass.
- Method Overriding: Subclass redefines a superclass method.
Why inheritance is important?
There are several reasons why inheritance is important in Java.
- First, it allows us to reuse code. This can save us a lot of time and effort, as we don’t have to rewrite code that already exists.
- Second, inheritance can help us to organize our code in a logical way. By grouping related classes together, we can make our code easier to understand and maintain.
- Third, inheritance can help us to create more complex and powerful classes. By inheriting from existing classes, we can add new features and functionality to our own classes.
Syntax of Inheritance in Java
Use the extends keyword to create a subclass:
class Vehicle { // Superclass
void start() {
System.out.println("Vehicle starts");
}
}
class Car extends Vehicle { // Subclass
// Inherits start() from Vehicle
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car myCar = new Car();
myCar.start(); // Output: Vehicle starts
}
} Types of Inheritance in Java
There are four types of inheritance:
- Single inheritance: This is the simplest type of inheritance. A subclass inherits from a single superclass.
- Multi-level inheritance: This is when a subclass inherits from another subclass.
- Hierarchical inheritance: This is when there is a hierarchy of classes, with each class inheriting from a single superclass.
Single-level inheritance
In single-level inheritance, a subclass inherits from a single superclass. This is the simplest type of inheritance, and it is the most common type of inheritance in Java.
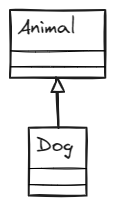
Example of single-level inheritance
The following code shows an example of single-level inheritance in Java:
class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Animal is eating");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public void bark() {
System.out.println("Dog is barking");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.eat();
dog.bark();
}
}
In this code, the Dog class inherits from the Animal class. This means that the Dog class inherits all of the methods and fields of the Animal class. In the main() method, we create a Dog object and call the eat() and bark() methods. The eat() method is inherited from the Animal class, and the bark() method is a method that is specific to the Dog class.
Multi-level inheritance
In multi-level inheritance, a subclass inherits from another subclass. This is a more complex type of inheritance than single-level inheritance, but it can be very useful for organizing our code.
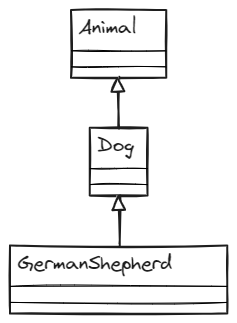
Example of multi-level inheritance
The following code shows an example of multi-level inheritance in Java:
class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Animal is eating");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public void bark() {
System.out.println("Dog is barking");
}
}
class GermanShepherd extends Dog {
public void herd() {
System.out.println("German Shepherd is herding");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GermanShepherd shepherd = new GermanShepherd();
shepherd.eat();
shepherd.bark();
shepherd.herd();
}
}
Hierarchical inheritance
In hierarchical inheritance, there is a hierarchy of classes, with each class inheriting from a single superclass. This is a more complex type of inheritance than single-level or multi-level inheritance, but it can be very useful for organizing our code.
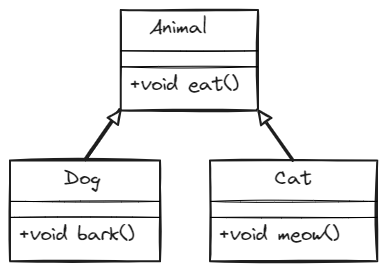
Example of hierarchical inheritance
The following code shows an example of hierarchical inheritance in Java:
class Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Animal is eating");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public void bark() {
System.out.println("Dog is barking");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public void meow() {
System.out.println("Cat is meowing");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
dog.eat();
dog.bark();
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.eat();
cat.meow();
}
}
In this code, we have three classes: Animal, Dog, and Cat. The Animal class is the superclass, and the Dog and Cat classes are subclasses. The Dog class inherits from the Animal class, and the Cat class inherits from the Animal class. This means that both the Dog and Cat classes can eat, as they inherit the eat() method from the Animal class. However, the Dog class can also bark, and the Cat class can also meow, as these are methods that are specific to each subclass.
Multiple inheritance
In multiple inheritance, a subclass inherits from multiple superclasses. This is not supported in Java, as it can lead to ambiguity.
There is a separate post on why multiple inheritance is not supported in Java.
Best Practices for Inheritance in Java
- Use
@OverrideAnnotation: Avoid typos and ensure correct overriding. - Keep Hierarchies Shallow: Prefer composition for complex relationships.
- Design for Extension: Make superclasses abstract if they’re meant to be inherited.
- Avoid Public Fields: Encapsulate data with
privatefields and getters/setters.
Conclusion
Inheritance in Java empowers you to build modular, reusable code by leveraging hierarchical relationships. By mastering method overriding, the super keyword, and best practices, you’ll create scalable applications that are easy to maintain.
FAQs
Can a class inherit from multiple classes in Java?
No. Java supports single inheritance for classes (use interfaces for multiple inheritance).
What is the difference between super() and this()?
super(): Calls superclass constructor.this(): Calls another constructor in the same class.
Can constructors be inherited?
No. Subclasses must define their own constructors.