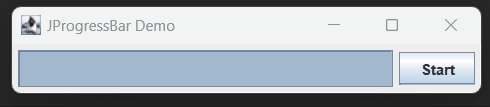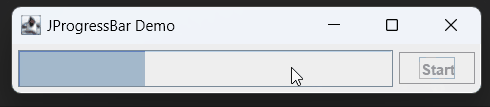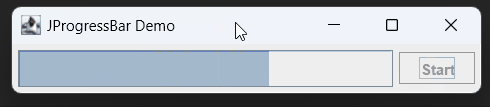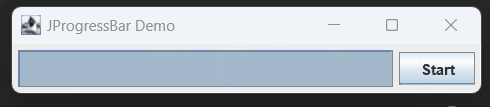
In Java, a JProgressBar is a graphical component that displays the progress of a task. It’s commonly used to show the advancement of tasks like file downloads, data processing, or any operation that takes time to complete.
Following a basic example of how to use the JProgressBar component:
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JProgressBar;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
import javax.swing.Timer;
public class JProgressBarDemo extends JFrame {
private JProgressBar progressBar;
private JButton startButton;
private Timer timer;
private int progressValue = 0;
public JProgressBarDemo() {
setTitle("JProgressBar Demo");
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
progressBar = new JProgressBar(0, 100);
progressBar.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(300, 30));
add(progressBar);
startButton = new JButton("Start");
add(startButton);
startButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
startButton.setEnabled(false); // Disable the button during progress
timer.start(); // Start the timer to update the progress
}
});
timer = new Timer(100, new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (progressValue < 100) {
progressValue++;
progressBar.setValue(progressValue);
} else {
timer.stop(); // Stop the timer when progress reaches 100
startButton.setEnabled(true); // Re-enable the button
progressValue = 0; // Reset progress for future use
}
}
});
pack();
setLocationRelativeTo(null); // Center the window
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
new JProgressBarDemo().setVisible(true);
}
});
}
}Output: