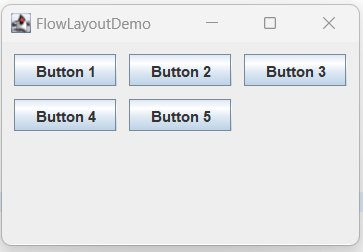
FlowLayout is a layout manager in Java Swing that arranges components in a row, wrapping to the next row if necessary. The components are laid out from left to right, with a default gap of 5 pixels between them.
To use FlowLayout in our Java Swing application, we can create a new instance of the FlowLayout class and set it as the layout manager of a container such as a JPanel.
Following is an example to use FlowLayout in Java Swing:
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class FlowLayoutDemo extends JPanel {
public FlowLayoutDemo() {
// Create a new FlowLayout with left alignment and a 10-pixel gap between
// components
FlowLayout layout = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT, 10, 10);
setLayout(layout);
// Add some components to the panel
add(new JButton("Button 1"));
add(new JButton("Button 2"));
add(new JButton("Button 3"));
add(new JButton("Button 4"));
add(new JButton("Button 5"));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setTitle("FlowLayoutDemo");
frame.add(new FlowLayoutDemo());
frame.setSize(300, 200);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Output: